
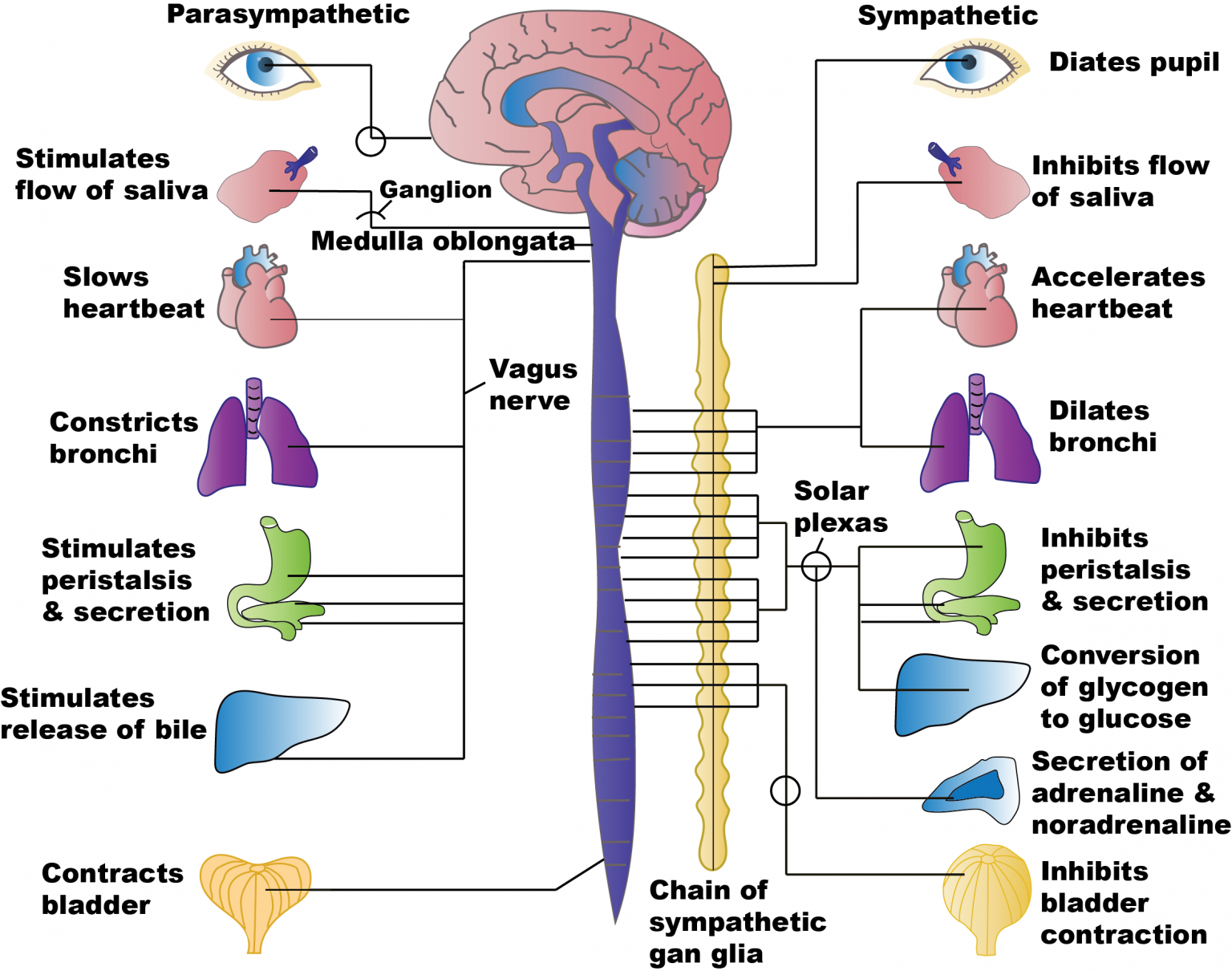
Oligodendrocytes - neuroglial cells of ectodermal origin that myelinateĪxons in the central nervous system and forms the white matter of the central.Protect, nourish, and maintain the neurons (Fig. Neuroglia - cells in the central nervous system that help to support,.Node of Ranvier - regions of the axon that lie between the SchwannĬells where the plasma membrane of a myelinated axon is close to the extracellular.Myelin sheath acts as an insulator that increases the rate of transmission Having myelinated an axon, lies on the surface of the myelin sheath - the That form a thin sheath that surrounds an unmyelinated axon, or, after In line causing the impulse to be sent by the postsynaptic nerve cell Neurotransmitters are released when the nerve impulse reaches the telodendria,Īnd then cross the synaptic cleft to reach the dendrites of the next neuron (e.g., acetylcholine, noradrenaline, serotonin, dopamine) The telodendria contains synaptic vesicles that contain neurotransmitters Sodium pumped outside of cell and resting potential restoredīetween neurons, nerve impulse must travel across a space or synapse. Nerve impulse travels down the axon as a wave of depolarizationĤ. Ions rush into cell, membrane potential reversed and membrane is depolarizedģ.
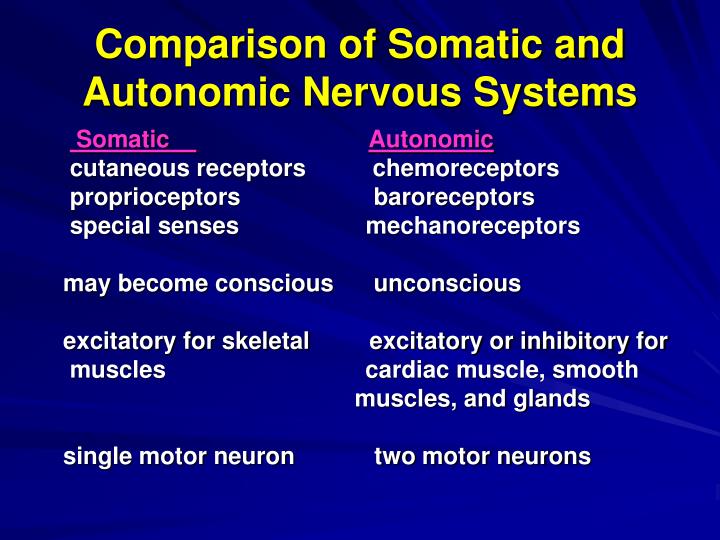

Axon stimulated, ion channels open causing action potential sodium High concentration of sodium ions outside negative charge insideĢ. Of sodium and potassium ions inside and outside of the cellĭuring an action potential, the neuron goes through several steps:ġ. Normally the nerve cell is at resting potential, based on the concentration The nerve impulse is an electrical phenomenon that passes as a waveĪlong the surface membrane of a nerve fiber Multipolar neurons - cell body lies very close to dendrites characteristic.Unipolar neurons - cell body lies off to one side of axon characteristic.Bipolar neurons - cell body located near the middle of the axon.The types of neurons in the body include: Ganglia - groups of neuron cell bodies that lie peripheral to the.Telodendria (transmissive) - the terminal branches of an axon make.Axon (conductive) - a long cytoplasmic process also called the nerveįiber can transmit nerve impulses over a long distance (up to 1 m) withoutĭiminution of the amplitude of the signal.Dendrites (receptive) - form extensions into tissues that may synapse.Cell body (trophic) - contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery.Neurons are derived from ectoderm from the neural tube, neural crest the peripheral nervous system - the cranial and spinal nervesĪll parts of the nervous system are composed of a common cellular subunit.the central nervous system - the brain and spinal cord.The primary components of the nervous system are: It also acts as a messenger and coordination system for the body The nervous system determines responses of the body to changes in internal The nervous system is the most complex system of the body, yet it is


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
